Declare and Set Worksheet
To be able to operate on a worksheet using VBA you have to specify which worksheet. Below discusses the many ways you can do this. If you use the Code VBA add-in using Set will add the declaration automatically. The below sections give an overview of the ways to Set a Worksheet variable from the available ones (see also Setting a Worksheet you just added.) In the code examples in the next sections the name of the worksheet variable is kept simple to 'ws' and its declaration is ignored:
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws =
| Tip |
|---|
| Shift-SPACE after the = in a Set statement opens the Set menu for the type, allowing you to select the appropriate statement (assuming Code VBA is installed) |
Using the ActiveSheet method to Set a variable
The method ActiveSheet gives you direct access to the currently active worksheet.
This sheet is the most likely one when working from a macro on a button on a Worksheet,
or when you are writing a general purpose add-in. In such a case however there is little reason to add an extra worksheet variable,
working from ActiveSheet directly is more direct. the default use is Application.ActiveSheet, alternatives are ActiveWindow.ActiveSheet and
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb =
Dim wsActiveSheet As Worksheet
Set wsActiveSheet = wb.ActiveSheet
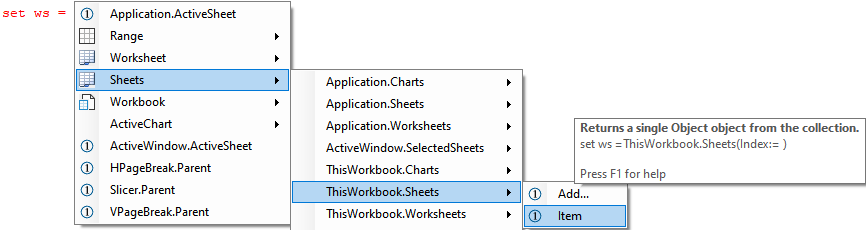
Set a variable to a Worksheet in a Sheets collection in a specified workbook
Often, you will want to Set a variable to a Worksheet in a Worksheets or Sheets collection of a Workbook. The submenu from Sheets lets you get the code
Set Worksheet in a specified workbook - by name
If you write macros for a specific line of business, your worksheet actions will generally assume a specific (type of) workbook as it's context. As an example, below code could be included in an Excel file with a worksheet called Locations. If your macro would involve more worksheets, you would probably name the variable wsLocations.
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb = ThisWorkbook
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = wb.Sheets("Locations")
If ws Is Nothing Then
Exit Sub 'possible way of handing no worksheet was set
End If
Returns Nothing if no sheet exists with that name. In fact any approach that tries to return a worksheet may return Nothing, so you should always check if a valid worksheet was set.
| Note |
|---|
| ws and wb are commonly used short names and prefixes for Worksheet and Workbook |
Using the Parent Worksheet of a Range
Sometimes, your macro uses multiple range variables located on different worksheets. Both the Parent and the Worksheet Method give access to the Worksheet object.
Previous and Next Worksheet
You can also Set a Worksheet variable to a Previous or Next worksheet, as seen from a specified Worksheet.
Parent property of a PageBreak object
Dim hpgbr As HPageBreak: Set hpgbr =
Dim wsParent As Worksheet
Set wsParent = hpgbr.Parent